Human skin suppresses inflammation after exposure to ultraviolet
4.6 (440) · € 5.50 · En stock
A study led by an NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre scientist has identified, for the first time, how the human skin suppresses inflammation after exposure to ultraviolet radiation (UVR). Dr Nathan Hawkshaw is the lead author of a research paper published in Clinical & Translational Immunology, an open access, peer-reviewed journal.

Astaxanthin: A natural remedy for Radiant Skin
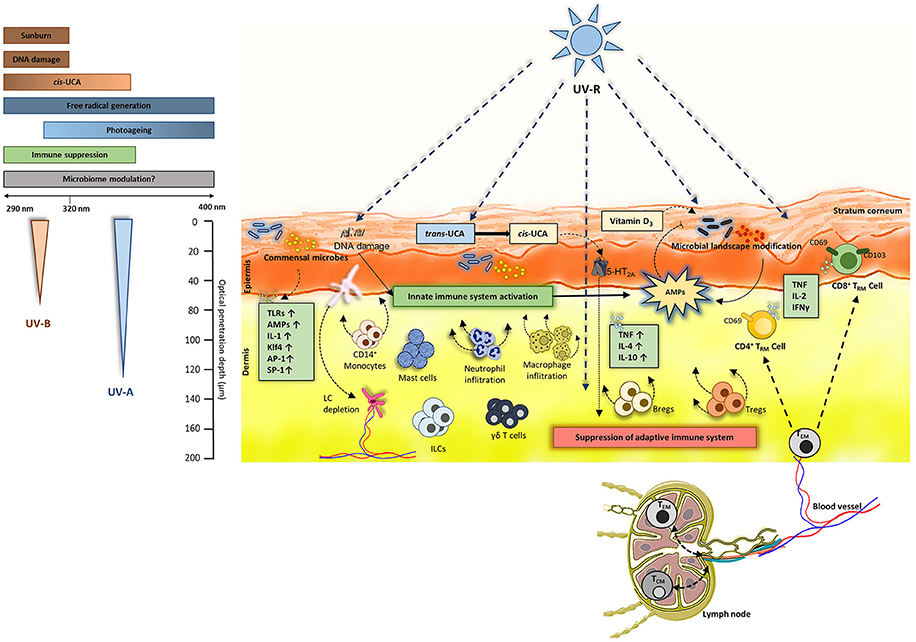
Frontiers A Perspective on the Interplay of Ultraviolet-Radiation, Skin Microbiome and Skin Resident Memory TCRαβ+ Cells

Skin Microbiome Modulates the Effect of Ultraviolet Radiation on Cellular Response and Immune Function - ScienceDirect

Crosstalk Among UV‐Induced Inflammatory Mediators, DNA Damage and Epigenetic Regulators Facilitates Suppression of the Immune System - Prasad - 2017 - Photochemistry and Photobiology - Wiley Online Library

Carbon dioxide inhibits UVB-induced inflammatory response by activating the proton-sensing receptor, GPR65, in human keratinocytes

Sunburn - Wikipedia

Frontiers Ultraviolet Radiation and Melanomagenesis: From Mechanism to Immunotherapy

Sunburn is not a useful indicator of immunosuppression in skin types

Ultraviolet-induced immune suppression. Exposure to UV-R results in DNA
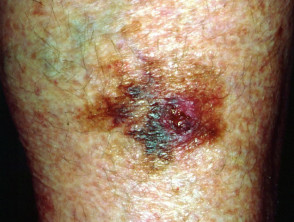
Ultraviolet radiation and human health

Soothe Sunburn: 5 Effective Remedies
Ultraviolet radiation and human health
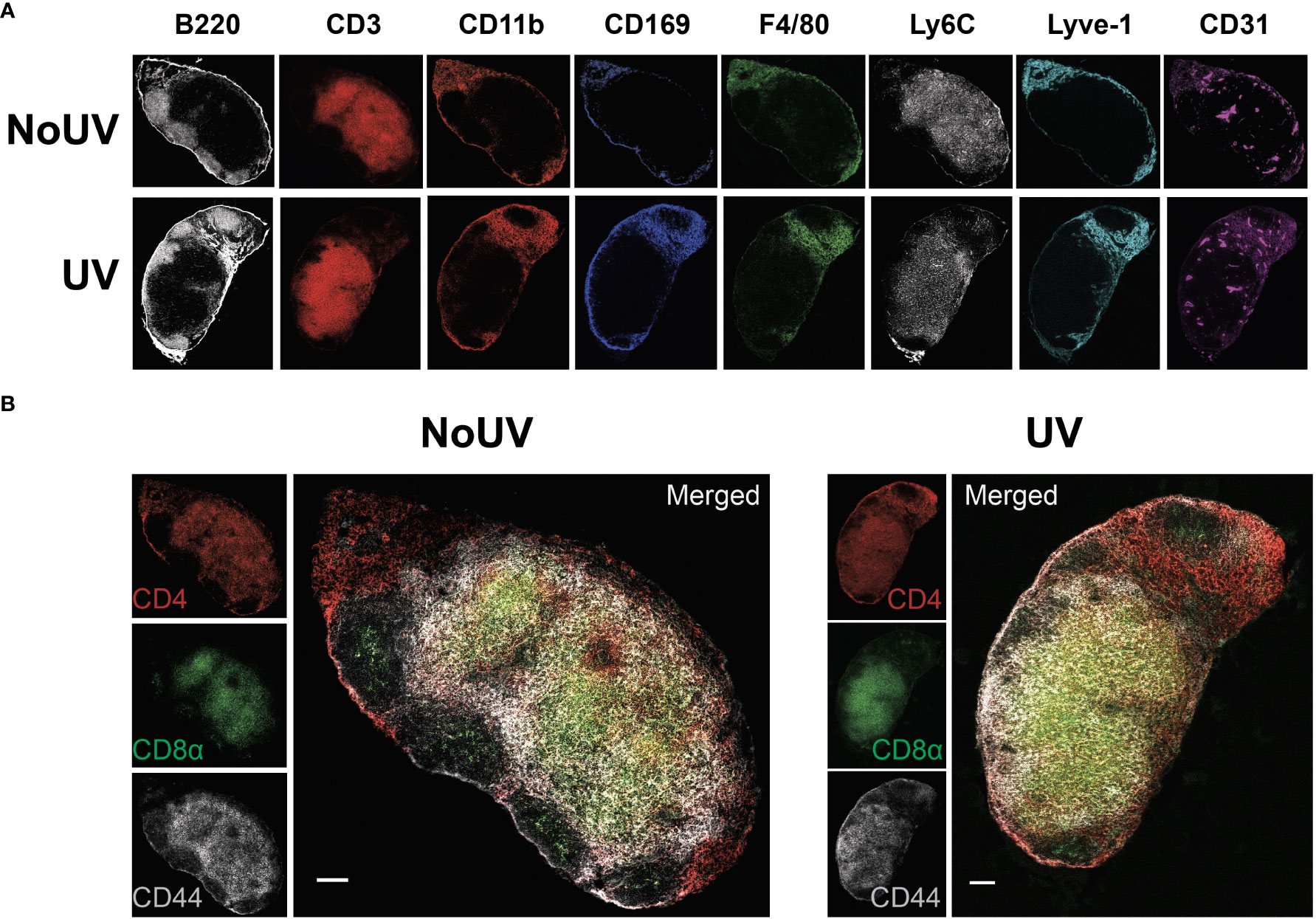
Frontiers Exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation establishes a novel immune suppressive lipidome in skin-draining lymph nodes

Particulate matter-induced skin inflammation is suppressed by polyphenol-enriched dietary supplement via inhibition of the AhR/ARNT signaling pathway - ScienceDirect

4‐phenylpyridine suppresses UVB‐induced skin inflammation by targeting c‐Src in vitro and in vivo - Kim - 2022 - Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine - Wiley Online Library












